The scanner heads can deflect the laser beam in the X and Y directions. This will create a two-dimensional planar area where the laser beam can be focused anywhere on this two-dimensional plane. This two-dimensional plane area is the marking range.
Laser beam deflection is achieved by two scanning galvanometer mirrors. The scan head has two holes, one for light input and another for light output. The laser beam enters the scan head from the input hole, and emit out from the output hole after deflected, as shown in Figure 1. Output hole open or install F-Theta scan lens or install protection window.
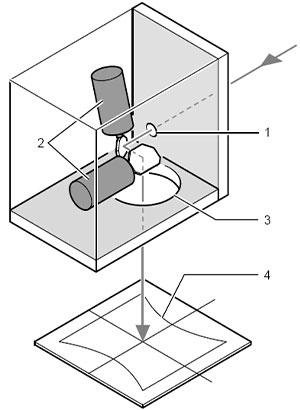
3-Axis Galvo Scan Head uses XY galvo and Z lens to form 3D dynamic focusing technology, which solves the problem that the focal spot on the marking plane becomes larger and the marking line width is different because the focal plane is spherical and the workpiece surface is flat after the laser beam passes through the focusing mirror. By changing the position of the dynamic focusing mirror, its focus is still on the surface of the workpiece, so as to achieve the effect of the same diameter and small diameter of all the spots in the marking range. The XY galvo scanner plays a crucial role in achieving these outcomes.